
How to design the fire alarm system for logistic facilities
December 1, 2023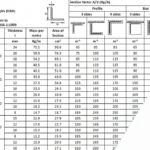
Engineering Fire Safety – Calculation Hp-A
December 1, 2023
How to design the fire alarm system for logistic facilities
December 1, 2023
Engineering Fire Safety – Calculation Hp-A
December 1, 2023Technical Library
Analyzing Flame Detector Failure
Analyzing Flame Detector Failure: Technical Insights into Causes and Mitigation Strategies
Introduction:
Flame detectors are integral components in fire detection and protection systems, serving as the first line of defense against potential fires in various industrial and commercial settings. However, like any technological system, flame detectors are susceptible to failure, and understanding the technical intricacies behind these failures is crucial for maintaining the reliability of fire safety systems. This article delves into the technical aspects of flame detector failures, exploring common causes and proposing mitigation strategies to enhance their performance.
Sensor Contamination:
1-Dust and Dirt Accumulation:
-
- Flame detectors are sensitive optical devices that can be affected by the accumulation of dust and dirt on their sensors.
- Contaminants may reduce the detector's sensitivity and responsiveness, leading to false positives or, more critically, failure to detect actual flames.
2-Environmental Factors:
-
- Harsh environmental conditions, such as high humidity, corrosive substances, or extreme temperatures, can contribute to sensor contamination.
- Protective enclosures and regular cleaning protocols are essential to mitigate these environmental challenges.
Optical Interference:
1-Sunlight and Artificial Light Sources:
-
- Natural sunlight or artificial light sources within the detection range can interfere with flame detectors, causing false alarms or inhibiting their ability to detect flames.
- Proper positioning and shielding can help minimize the impact of external light sources on detector performance.
2-Reflected Light:
-
- Reflections from shiny or polished surfaces can create false positives by mimicking the appearance of flames.
- Detector placement and angle adjustments are critical to avoid erroneous readings caused by reflected light.
Sensor Degradation:
1-Aging and Wear:
-
- Over time, the optical components of flame detectors may degrade due to exposure to environmental conditions, leading to reduced sensitivity.
- Regular inspection and replacement of aging components can help maintain optimal detector performance.
2-Material Erosion:
-
- Detectors installed in environments with abrasive particles or corrosive substances may experience material erosion, impacting their longevity and effectiveness.
- Selecting flame detectors with robust materials or implementing protective measures is essential in such environments.
Electrical and Electronic Failures:
1-Power Supply Issues:
-
- Flame detectors rely on a stable power supply, and any disruptions or fluctuations may result in operational failures.
- Implementing backup power systems and surge protection can mitigate the risks associated with power supply issues.
2-Electronic Component Failure:
-
- Electronic components, including circuit boards and processors, may fail due to manufacturing defects, electrical surges, or environmental stress.
- Regular testing and quality assurance measures during manufacturing and maintenance are crucial for detecting and addressing potential electronic failures.
Maintenance and Testing Neglect:
1-Infrequent Testing:
-
- Failure to conduct regular testing and maintenance routines can lead to undetected issues with flame detectors.
- Establishing a comprehensive testing schedule and adhering to manufacturer recommendations are vital for ensuring detector reliability.
2-Calibration Errors:
-
- Inaccurate calibration can compromise the sensitivity and responsiveness of flame detectors.
- Regular calibration checks and adjustments based on environmental conditions and the specific application are essential for optimal performance.
Conclusion:
Flame detector failures can have severe consequences for fire safety systems, underscoring the importance of a proactive and technical approach to address potential issues. Recognizing the causes of failure, from sensor contamination to electronic component issues, enables operators to implement targeted mitigation strategies. By prioritizing regular maintenance, testing, and adherence to best practices, industries can enhance the reliability of flame detectors and, in turn, fortify their overall fire protection measures.
