Passive Fire Protection Systems
Structural Steel Protection
Intumescent
Coatings

Intumescent paints - efficient way of protection of steel materials against fire
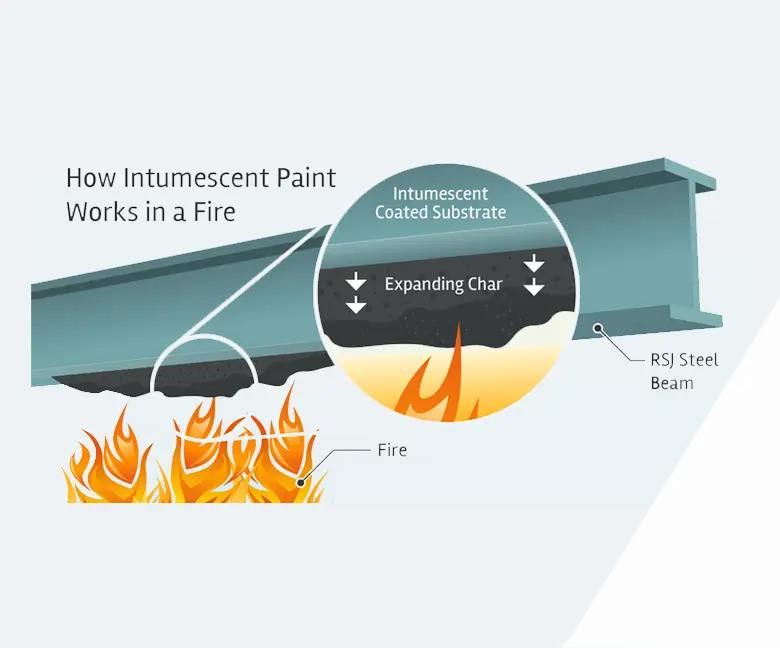
Intumescent coating, often referred to as intumescent paint, is one of the easiest and most efficient ways to protect load-bearing elements of buildings against fire. Intumescent coating delays the collapse of the structure through insulating the structural elements (columns, beams, floors and roofs) that support the building, thus helping achieve fire resistance levels specified in terms of time. Therefore, it fulfills the highest priority of passive fire protection: preventing the collapse of the building, allowing the time for safe evacuation of people from it and making it safer for the emergency services and rescue team.
Intumescent coating is an increasingly used way of providing passive fire protection to the load-bearing structures, especially structural steel, which is becoming more and more popular in modern architectural design of both industrial and commercial buildings. As a means of fire protection, intumescent coating presents several advantages:
It does not modify the intrinsic properties of materials, for example, the mechanical properties; It is easily processed, also intumescent steel coatings provide Good aesthetic finish and adaptability to the shape of steel, Cost-Effectiveness and easy maintenance.
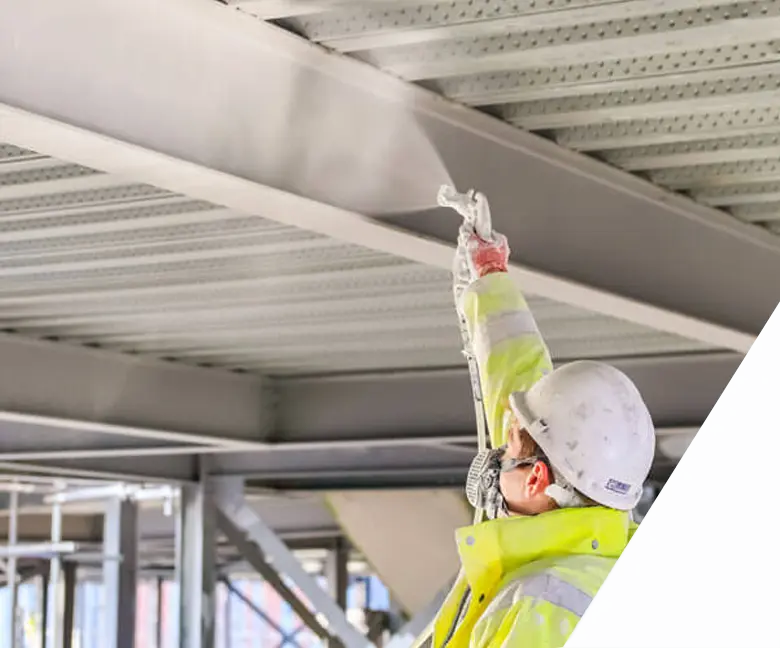

How to correctly apply intumescent paints to steel materials - preparation tips
Intumescent paints are always part of a system. For steelworks, the system includes an anticorrosive primer and (eventually) a topcoat. For the former, the purpose is assuring adhesion to the substrate in the cold state, anticorrosion protection and stickability of intumescent char formed during fire exposure, while for the latter, the purpose is serving an aesthetic function and, in case of specific atmospheric aggression, a sealer function to prevent early degradation and inactivation of the intumescent layer and to promote weathering resistance in end-use conditions.
Before being coated with a compatible primer, steelwork must be prepared according to the SA 2.5 Swedish Standard. If that is already the case, it must be cleaned and free from grease, oil, rust, dirt or any other contaminant that may inhibit the bonding.
Have Questions?
Contact Us